Dr. Marc-Ansy Laguerre’s Teaching Philosophy
Teaching with Purpose: Guiding Growth, Connection, and Application
My teaching rests on four core principles: centering students, promoting a growth mindset, recognizing the role of emotions in learning, and bridging theory with practice. I aim to create a supportive environment where students feel valued, challenged, and empowered to apply their learning in meaningful ways.
Student-Centered Approach
I strive to place students at the heart of my teaching. I recognize that each learner comes with a unique background, set of interests, and way of engaging with material. My role is to guide, support, and create the conditions in which their learning can truly take root.

Growth Mindset and High Expectations
I believe intelligence is not fixed—it can grow. That’s why I intentionally promote a growth mindset, both for my students and for myself. I set high expectations not to overwhelm, but to encourage and inspire

Emotions as Catalysts for Learning
I see emotions not as distractions, but as vital drivers of learning. I’m naturally quiet and reflective, and I try to create a calm learning environment where students can feel comfortable, supported, and confident in themselves.

Bridging Theory and Practice to Foster Deep Learning
I design my teaching to help students move from abstract concepts to real-world application. Whether through hands-on experiments, software demonstrations, or videos, I aim to make learning tangible.
Fulbright Fellowship (2017-2019)
Dr. Marc-Ansy Laguerre is a Fulbright Fellow who pursued graduate studies at the University of Pittsburgh, earning a master’s degree in civil engineering and a Graduate Certificate in Latin American Social and Public Policy. His academic journey reflects a strong commitment to interdisciplinary learning, international collaboration, and advancing engineering solutions for societal resilience.

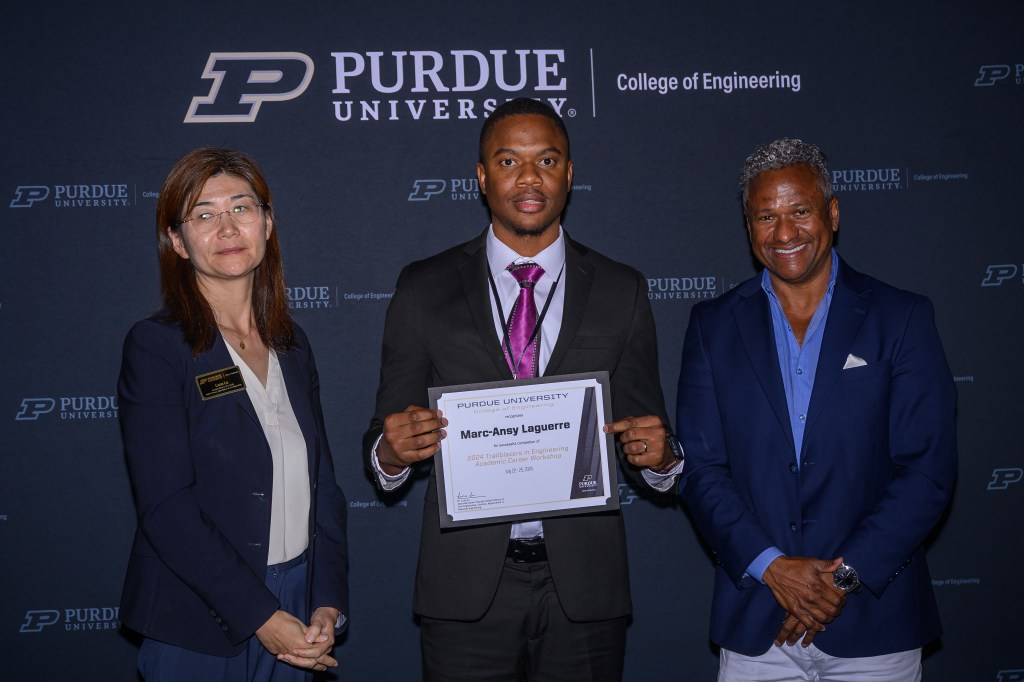
Purdue Trailblazers in Engineering Fellow 2024
Dr. Marc-Ansy Laguerre was selected as a 2024 Purdue Trailblazers in Engineering (TBE) Fellow, a prestigious program recognizing early-career researchers committed to academic excellence, innovation, and inclusive leadership in engineering. This fellowship supports future faculty through professional development, mentorship, and national visibility within the engineering education community.

Quotes That Resonate
These quotes have accompanied me on my path as an educator. They don’t stand alone; they’re part of a broader reflection shaped by experience, emotion, and ongoing learning. Inspired by Parker Palmer, Susan Ambrose and Ken Bain, they speak to the heart of what I value: teaching that connects, challenges, and nurtures both the mind and the person.

Academics often suffer the pain of dismemberment. On the surface, this is the pain of people who thought they were joining a community of scholars but find themselves in distant, competitive, and uncaring relationships with colleagues and students. Deeper down, this pain is more spiritual than sociological: it comes from being disconnected from our own truth, from the passions that took us into teaching, from the heart that is the source of all good work.
Parker J. Palmer, The Courage to Teach

To take a deep approach means to take control of your own education, to decide that you want to understand, to create something new, to search for the meaning that lies behind the text, to realize that words on a page are mere symbols, and that behind those symbols lies a meaning that has a connection with a thousand other aspects of life and with your own personal development.
Ken Bain, What the Best College Students do

… two considerations are important when dealing with college students. First, emotional and social processes are particularly salient during this phase of life. In fact, a preponderant body of research documents that the social and emotional gains that students make during college are considerably greater than the intellectual gains over the same span of time (Pascarella & Terenzini, 1991). Second, these emotions can overwhelm students’ intellect if they have not yet learned to channel them productively.
Susan A. Ambrose et al., How Learning Works
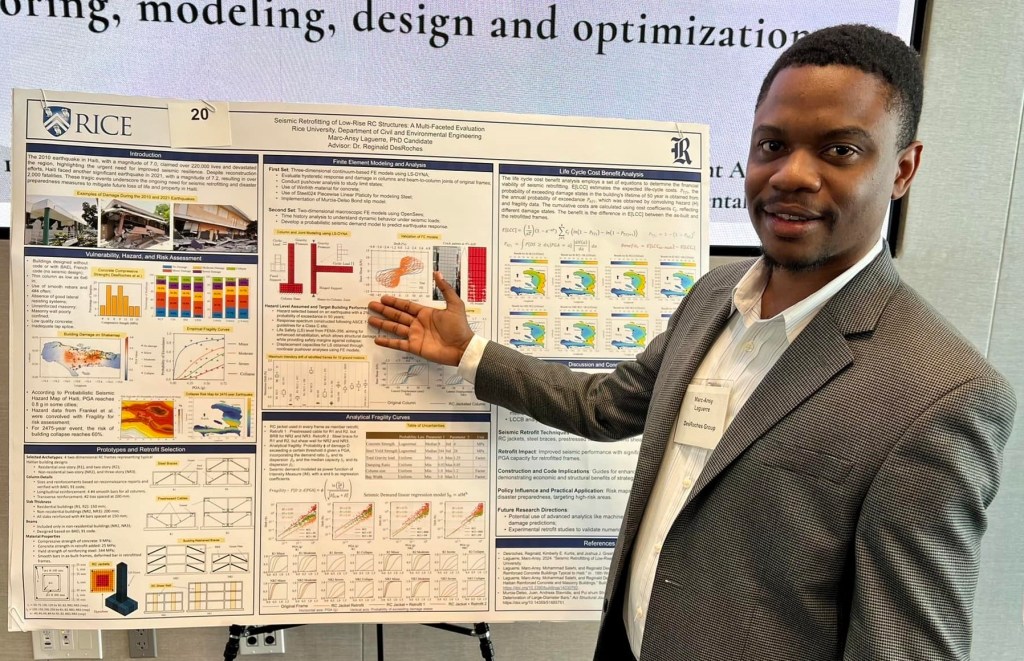
Research Industry Showcase at Rice University 2024
In 2024, Dr. Marc-Ansy Laguerre participated in the Rice University Research & Industry Showcase, where he presented a poster on his work comparing empirical and analytical fragility assessments of reinforced concrete buildings in Haiti. His research highlights the use of post-earthquake data and simulation-based modeling to evaluate seismic vulnerability and inform retrofit strategies.
Hands-On Seismic Learning
Dr. Marc-Ansy Laguerre uses a structural kit to perform hands-on experiments that illustrate how buildings behave under earthquake forces, making complex structural concepts easier to understand through physical demonstration.

Reflections
Discover my latest blog post where I share reflections, insights, and ideas that bridge engineering, education, and social impact. I’d love to hear your thoughts!